Living with ADHD can be challenging, but Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers effective tools to manage its symptoms. By focusing on changing thought patterns and developing practical strategies, CBT empowers individuals to gain better control over their daily lives. In this article, we will explore powerful CBT exercises for ADHD that can help improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and build healthier habits for long-term success.
What is CBT and How Does It Help ADHD?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a structured, goal-oriented form of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. For individuals with ADHD, CBT is particularly effective in addressing challenges like impulsivity, disorganization, and emotional regulation. Unlike traditional therapy, which may delve into past experiences, CBT emphasizes actionable strategies that help individuals tackle specific issues in their daily lives.
CBT helps individuals with ADHD by teaching skills to improve focus, manage time effectively, and reduce procrastination. It also equips them with techniques to handle emotional outbursts, boost self-esteem, and create healthier habits. By implementing targeted CBT exercises for ADHD, individuals can gradually develop better control over their symptoms and achieve greater success in personal and professional areas.
Top 5 CBT Exercises for ADHD You Can Try Today
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers practical tools to help individuals with ADHD manage their symptoms effectively. Here are five simple yet impactful CBT exercises for ADHD that you can start incorporating into your daily routine today:
- Thought Journaling: Keep a journal to track your thoughts and emotions throughout the day. Write down situations where you felt overwhelmed or distracted, and identify any negative thought patterns. Reflecting on these can help you reframe your thoughts and respond more calmly to challenges.

- Task Chunking : Break down overwhelming tasks into smaller, manageable steps. For instance, instead of clean the house,” start with “clear the living room table.” This technique helps reduce procrastination and builds momentum for completing larger goals.
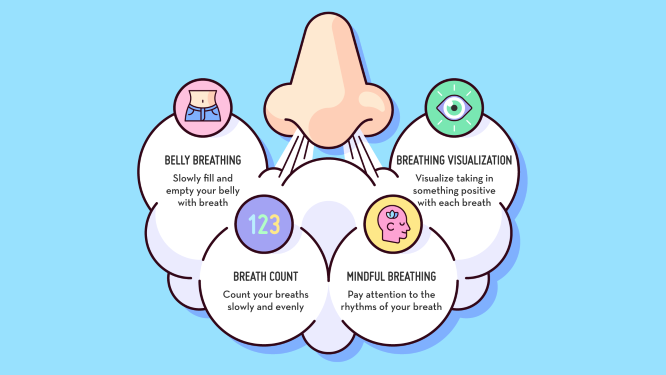
- Mindfulness Breathing: Practice focused breathing exercises to calm your mind and improve attention. Take deep breaths in and out, concentrating on your breath. This simple exercise reduces impulsivity and enhances self-awareness.
- Positive Affirmations: Create a list of affirmations that challenge negative self-talk. For example, replace “I always mess up” with “I am capable of learning and improving.” Repeating these affirmations daily helps build self-confidence and reduces feelings of frustration.

- Reward-Based Motivation: Set up a reward system for completing tasks. For example, if you finish your work on time, treat yourself to something enjoyable. This technique leverages the ADHD brain’s need for immediate gratification and boosts productivity.

These CBT exercises for ADHD are easy to implement and can make a big difference when practiced consistently. They empower you to take control of your thoughts, emotions, and actions, leading to improved focus and overall well-being.
The Science Behind CBT exercises for ADHD Symptom Management
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a scientifically supported approach that helps individuals with ADHD address their challenges by focusing on thought patterns and behaviors. Research shows that ADHD symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation can be effectively managed through structured CBT techniques. These techniques are designed to reframe negative thinking, establish productive habits, and reduce stress.
One of the core aspects of CBT is its focus on practical strategies, such as CBT exercises for ADHD, which empower individuals to take control of their symptoms. These exercises target key issues like improving focus, enhancing time management, and managing emotional responses. By combining behavioral strategies with cognitive reframing, CBT offers a holistic way to manage ADHD symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Read Also : ADHD Music: Everything You Need to Know
Step-by-Step Guide: CBT Exercises for ADHD
Managing ADHD can feel overwhelming, but breaking it down into actionable steps can make a significant difference. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers practical solutions to tackle the daily challenges associated with ADHD. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll explore some effective CBT exercises for ADHD that can help improve focus, organization, and emotional regulation.
- Identify Triggers
Begin by observing situations or patterns that trigger impulsivity or distractibility. Use a journal to document these moments, helping you recognize recurring themes. - Reframe Negative Thoughts
Practice replacing negative self-talk, such as “I can’t do anything right,” with constructive statements like “I’m learning and improving.” This builds a more positive mindset. - Break Tasks into Small Steps
Use task chunking to divide overwhelming tasks into smaller, manageable parts. For example, instead of “clean the house,” start with “organize the bookshelf.” - Practice Mindfulness Breathing
Spend a few minutes each day on mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing. This helps calm your mind and increase your ability to focus. - Reward Progress
Set up a reward system to celebrate small victories. Completing a task or sticking to a plan can be followed by a treat, boosting motivation and reinforcing positive behavior.
These CBT exercises for ADHD are easy to follow and can be integrated into daily routines. With consistent practice, they can help you gain better control over ADHD symptoms and lead a more productive, balanced life.
Benefits of Using CBT for ADHD Treatment
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a powerful tool for managing ADHD symptoms, providing individuals with practical strategies to navigate daily challenges. Unlike medication, which primarily addresses chemical imbalances, CBT focuses on behavioral and cognitive adjustments, empowering individuals to take control of their actions and thoughts. Here are some key benefits of using CBT for ADHD treatment:
- Improved Emotional Regulation
CBT helps individuals identify and manage their emotional triggers, reducing impulsive reactions and improving self-control during stressful situations. - Enhanced Time Management Skills
Through structured CBT exercises for ADHD, individuals learn how to break tasks into smaller steps, set priorities, and use time effectively, leading to increased productivity. - Reduction in Procrastination
CBT teaches techniques to overcome procrastination, such as breaking down overwhelming tasks, setting deadlines, and rewarding progress. - Better Focus and Attention
By addressing negative thought patterns and creating actionable strategies, CBT improves focus and reduces distractibility, helping individuals stay on task. - Increased Self-Awareness
CBT encourages individuals to track their behaviors and thought processes, fostering a deeper understanding of their ADHD and how it impacts their daily lives. - Long-Term Coping Mechanisms
Unlike quick fixes, CBT equips individuals with long-lasting tools and habits to manage ADHD symptoms independently, providing lifelong benefits. - Boosted Self-Confidence
As individuals see progress through CBT, their self-esteem grows, helping them feel more capable of tackling challenges and achieving their goals.
Incorporating CBT into ADHD treatment plans can lead to significant improvements in quality of life. By focusing on practical, actionable strategies, CBT empowers individuals to overcome obstacles and thrive despite the challenges of ADHD.
Read Also : Top 10 Natural Adhd supplements for kids and Adult, What’s the difference?
How to Incorporate CBT Exercises for ADHD into Your Daily Routine
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an effective approach for managing ADHD symptoms, but its real power lies in consistent application. Integrating CBT exercises for ADHD into your daily life can transform how you handle distractions, procrastination, and emotional challenges. Here are practical ways to weave CBT techniques into your everyday routine:
- Start with Morning Planning
Begin your day with a brief session of goal-setting. Write down your priorities for the day and break larger tasks into smaller, actionable steps. This helps you focus on what’s important and reduces feelings of being overwhelmed. - Use Thought Journaling
Throughout the day, jot down instances where you feel distracted or stressed. Reflect on these moments, identify negative thought patterns, and practice reframing them into positive, constructive thoughts. - Practice Mindful Breathing During Breaks
Incorporate mindfulness exercises during short breaks. For example, take five minutes to focus on deep breathing, which can help center your mind and improve focus. - Create a Reward System
Set up small rewards for accomplishing tasks or sticking to your plans. Whether it’s enjoying a favorite snack or watching a short video, rewards can motivate you to stay consistent with CBT strategies. - Set Reminders for Check-Ins
Use phone alarms or apps to schedule moments during the day to pause and evaluate your progress. These check-ins can help you realign your focus and remind you to practice CBT techniques, such as challenging negative thoughts. - Wind Down with Reflection
At the end of the day, spend a few minutes reviewing what went well and what could be improved. Reflecting on your successes and challenges reinforces positive habits and helps you refine your CBT exercises for ADHD. - Make It a Routine
Consistency is key. Start small by introducing one or two exercises at a time and gradually build up as they become habits. The more naturally these techniques fit into your routine, the easier they are to maintain.
By incorporating CBT exercises for ADHD into your daily life, you can build a structured, supportive routine that empowers you to manage your symptoms effectively. Over time, these small changes can lead to significant improvements in focus, productivity, and emotional balance.

Quick CBT Techniques to Improve Focus and Reduce Impulsivity
Managing focus and impulsivity can be challenging for individuals with ADHD, but Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers simple and effective tools to help. Here are some quick CBT exercises for ADHD that you can use daily to improve focus and control impulsive behaviors:
- The 5-Minute Rule
Struggling to start a task? Commit to working on it for just five minutes. Often, this small commitment helps overcome procrastination, and once you’ve started, you’re more likely to keep going. - Stop and Breathe
When you feel the urge to act impulsively, pause for a moment and take five deep breaths. This simple mindfulness exercise calms your mind and gives you time to assess your actions before responding. - Thought Stopping
If a distracting or negative thought pops up, visualize a stop sign or say “stop” out loud. Then, replace the thought with a more constructive one, such as focusing on the next step of your task. - Chunk Your Tasks
Break large tasks into smaller, more manageable parts. Completing one small section at a time reduces overwhelm and keeps your focus sharp. - Visual Reminders
Use sticky notes or visual cues around your workspace to keep your goals in mind. For example, a note saying “Focus on one task at a time” can serve as a gentle reminder. - Impulse Journaling
Carry a small notebook or use a phone app to jot down impulsive thoughts or urges as they occur. Writing them down gives you time to process the impulse without acting on it. - Use a Timer
Set a timer for 15-25 minutes and focus solely on your current task until the timer rings. This technique, similar to the Pomodoro method, helps create a sense of urgency and minimizes distractions. - Practice Gratitude Refocusing
When you feel overwhelmed, take a moment to list three things you’re grateful for. This shifts your focus from frustration to positivity and helps re-center your attention.
These quick CBT exercises for ADHD are simple yet powerful tools to help you stay focused and reduce impulsive actions. By incorporating them into your daily routine, you can gradually build better control over your thoughts and behaviors.
Tell us, did you use CBT exercises for ADHD before ? what do you think about the efficiency of this approach ?


